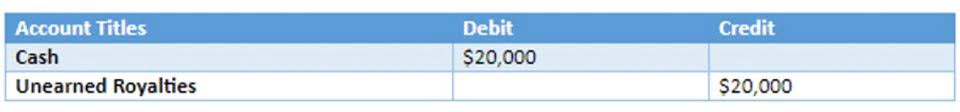
Before implementing, be brutally honest about whether you have the resources to do it right. A half-implemented standard costing system creates more problems https://www.byprojekt.com/2021/01/27/mastering-unearned-revenue-essential-accounting-10/ than it solves. Standard costing thrives in repetitive manufacturing environments where cost components remain stable. If you’re making the same products day in and day out, this system starts to shine.

What are the components of Standard Costing?
- This is the product’s labor requirement multiplied by the typical hourly wage you pay your employees.
- This can lead to unhealthy competition and encourage unethical behavior.
- Comparison and analysis of data – Standard costing provides a stable and sound basis for comparison of actual data with standard costs according to different elements separately.
- By delving into these underlying factors, businesses can identify specific areas that require attention and take corrective actions to improve performance.
It results in the reduction in paper work in accounting and needs very in a standard cost system, few records. To help the management in formulating production policy and helps in fixing the price quotations as well as in submitting tenders of various products. Through the application of this costing it can be ascertained whether or not the activities of production are going on according as the pre‐determined plan.
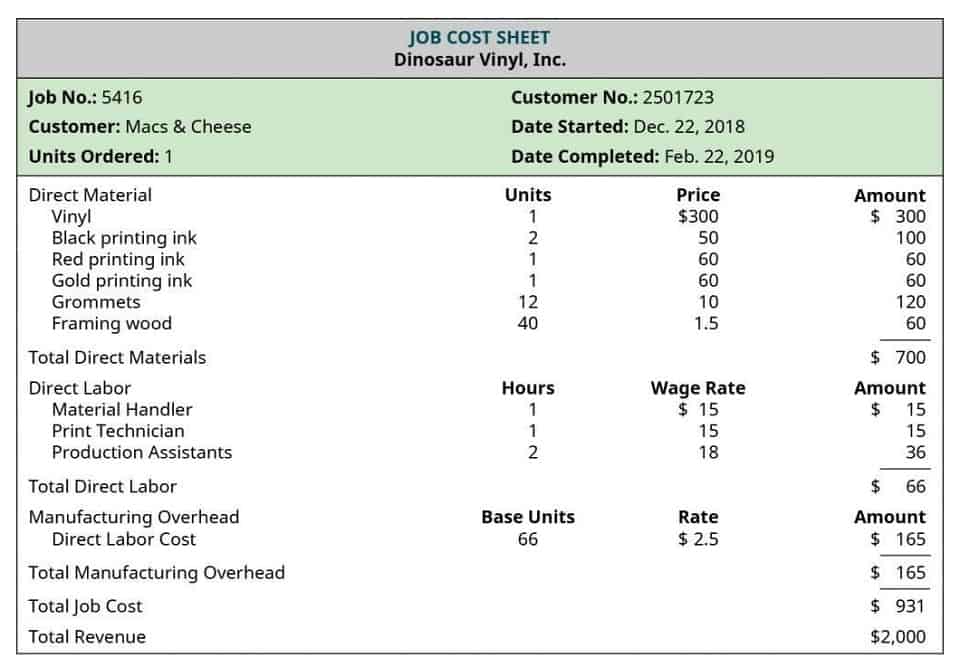
How does standard costing help a company achieve its goals?
If some of the operations applied to different products are common and repetitive, standards may be fixed for such components or operations with advantage. Travel Agency Accounting The cost-benefit analysis should however be made before installing a standard costing system. If the costs exceed benefits, no system can be recommended for adoption, not to talk of standard costing system.
- The standard direct materials cost perunit of a product consists of the standard amount of materialrequired to produce the unit multiplied by the standard price ofthe material.
- The features of standard costing are related to the objectives of standard costing.
- Budgeting is a process of planning and organizing your financial resources so that you can make informed decisions about where best to invest them.
- Then, to minimize variances as you produce more products, you can update this estimate based on your actual costs.
- Management will only look into unusual variances, so workers may retaliate by not reporting negative exceptions.
- One of the primary elements in standard costing is the establishment of standard material costs.
What is Standard Costing – Essential Conditions for Effective Standard Costing

Theprocess of management by exception enables management toconcentrate its efforts on those variances that could have a bigeffect on the company, ignoring those variances that are notsignificant. Proper configuration is essential—setting up accurate bills of materials, routing operations, cost centers, and allocation methods that reflect your production reality. Gone are the days of manually logging material usage or tracking labor hours on paper. Today’s systems automatically capture cost data throughout the production process—from material requisitions to labor time to machine utilization. When using standard costing, you must determine whether the return on your time and resource investments is worthwhile. Are operational or variances in production orders or individual items being actively reviewed, analyzed for trends, and used to inform improvements?
How to Interpret Variances
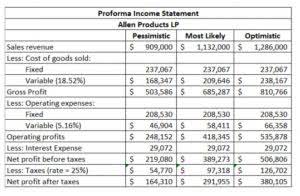
That part of a manufacturer’s inventory that is in the production process but not yet completed. This account contains the cost of the direct material, direct labor, and factory overhead in the products so far. A manufacturer must disclose in its financial statements the cost of its work-in-process as well as the cost of finished goods and materials on hand. It is assumed that the additional 8 hours caused the company to use additional electricity and supplies.
Are We Training Accountants for a Job AI Will Mostly Do?
- Accountants realize that this is simplistic; they know that overhead costs are caused by many different factors.
- Since the company must pay its vendors and production workers the actual costs incurred, there are likely to be some differences.
- When a company is manufacturing different types of products, it is almost impossible to increase the production, which cannot be expressed in the same unit.
- Most of these problems result from improper use of standard costs and the management by exception principle or from using standard costs in situations in which they are not appropriate.
- From daily operational choices to strategic initiatives, solid cost data provides the foundation for continuous improvement and competitive advantage in today’s manufacturing landscape.
Making an accurate estimate of the typical cost of a company’s service or product production is difficult because of the variety of factors that may be at play. Such costs must be calculated, and historical data and projected expenditure trends are needed. Standard costs give a broad overview of a company’s production division but don’t go into detail. They don’t provide enough detail to demonstrate how successfully your business produced a particular batch or unit of product.