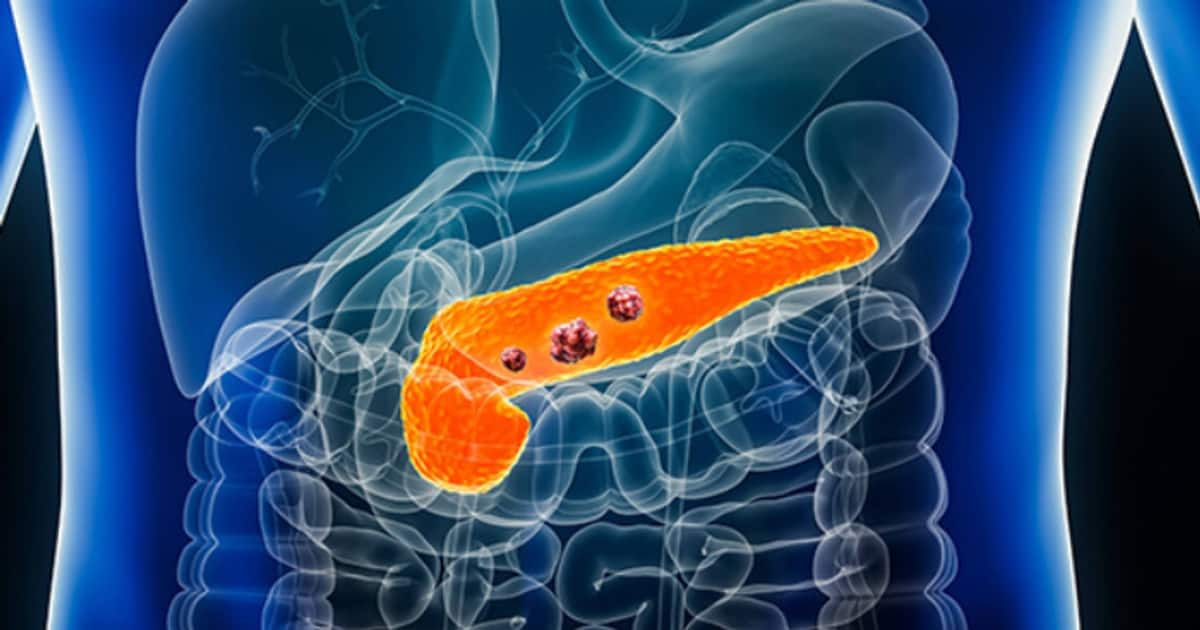
The two most common presentations of pancreatic cancer are abdominal or stomach pain and jaundice. Pancreas is broadly divided into 3 parts, i.e head, body and tail. Jaundice is most commonly seen in pancreatic head and body cancer, while pancreatic tail cancers present as pain in the left side of the abdomen.
How pancreatic cancer causes jaundice?
We must first understand bile flow’s anatomy and physiology to know this. Bile is produced in liver and stored in gall bladder and then through bile duct it comes down to mix with food to help in digestion. This bile duct comes through the pancreatic head before opening into the food pipe inside the duodenum. So when cancer occurs in the pancreatic head and neck, it gradually increases in size and involves and compresses the bile duct that passes through the pancreas. Thus bile cannot come down from liver and it gradually accumulates in the liver and get absorbed into the stream and causes jaundice
How is pancreatic jaundice different from jaundice seen in hepatitis or liver disease?
Jaundice in pancreatic cancer is called obstructive jaundice, while in hepatitis or liver failure, jaundice is called medical jaundice. In obstructive jaundice, it will be associated with generalised itching over body; jaundice will increase slowly, i.e fist, there will be yellow/brown coloured urine, then sclera (white part of eye will become yellow, the skin over palm & sole becomes yellow and last skin over whole body becomes yellow, stool colour will change to clay colour. When jaundice gets infected, it will cause fever with chills, severe upper abdominal pain, vomiting, and generalised weakness. Also in pancreatic cancer there will be decreased appetite and gradual weight loss.
How to treat jaundice in pancreatic cancer?
First, a CT scan or MRI scan is done to confirm the diagnosis that jaundice is due to pancreatic cancer. Then a gastro surgeon or g.i. oncosurgeon determines whether the tumour is operable or not. Surgical removal of pancreatic cancer is the best and only way to cure it. If cancer is not spread to other sites of the body and if jaundice is not very high, then the patient is directly operated on with whipped pancreatoduodenectomy surgery. If jaundice is very high or it is infected, then a gastroenterologist will do an ERCP and put a stent inside bile duct to decrease the jaundice and prepare the patient for surgery. After recovering from surgery patient is further treated with chemotherapy to maximize the survival years.
Lifestyle modification to lower risk of pancreatic cancer?
Risk factors for pancreatic cancer can be divided into two types. Modifiable and non-modifiable.
Modifiable risks are alcohol, smoking, consuming tobacco products, a diet rich in saturated fat, high red meat consumption like mutton or beef, smoked and salted food items like tandoori and consuming fewer fruits.
If we avoid these modifiable risk factors and live a healthy life with a diet rich in green/red vegetables and fruits, regular food habits, and exercise or yoga, we can decrease our risk of pancreatic cancer.
Non-modifiable risk factors include genetic mutation, family history, and belonging to a race prone to developing pancreatic cancer. Persons in these categories should get regular health checkups and avoid modifiable risk factors. A happy pancreas leads to a healthy life.
– Dr. Jyotirmay Jena, Consultant – G.I. & H.P.B Surgery, Manipal Hospital, Bhubaneshwar